AI scans arteries and predicts risk after heart attack better than traditional review and this innovation is transforming cardiovascular diagnostics. Advanced deep learning models applied to CT scans can detect hidden arterial features—plaque composition, arterial inflammation, microcalcifications—far beyond what traditional human review can assess. This capability enables personalized and highly accurate risk prediction. In this article, we explore seven pivotal findings supported by data and real-world studies that prove how AI is outperforming traditional evaluation.
AI Scans Arteries and Predicts Risk After Heart Attack Better Than Traditional Review Through Calcium Detection
A Mass General Brigham study developed AI‑CAC—an algorithm that analyzes routine chest CTs to quantify coronary artery calcium. The AI identified presence of CAC with 89.4% accuracy and whether CAC exceeded 100 (moderate risk) with 87.3% accuracy. Most importantly, a CAC score >400 correlated with a 3.49× higher 10‑year mortality compared to a zero score.
| AI-CAC Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Accuracy (CAC detection) | 89.4% |
| Accuracy (CAC > 100) | 87.3% |
| 10-year mortality risk (CAC >400 vs. 0) | 3.49× |
AI Scans Arteries and Predicts Risk After Heart Attack Better Than Traditional Review by Predicting Long-Term Events
Oxford research found that AI using routine cardiac CT scans could predict heart attacks, heart failure, or cardiac death up to 10 years in advance. Impressively, two-thirds of major cardiac events occurred in patients whose initial scans showed no significant arterial blockages.
This shift underscores an AI advantage: hidden indicators, like arterial inflammation, are catching future risk that traditional reviews miss.
AI Scans Arteries and Predicts Risk After Heart Attack Better Than Traditional Review via Calcium-Oomics
A novel “calcium-omics” model leveraging AI analyzes detailed features—calcification number, density, spatial distribution, plaque mass—to outperform traditional Agatston scoring. The AI model achieved AUC of 82.4% (two-year prediction) vs. 71.8% for Agatston, and reclassified 63% of MACE (major adverse cardiovascular events) patients into high-risk groups.
This clearly shows how AI’s nuanced data extraction elevates risk assessment accuracy.
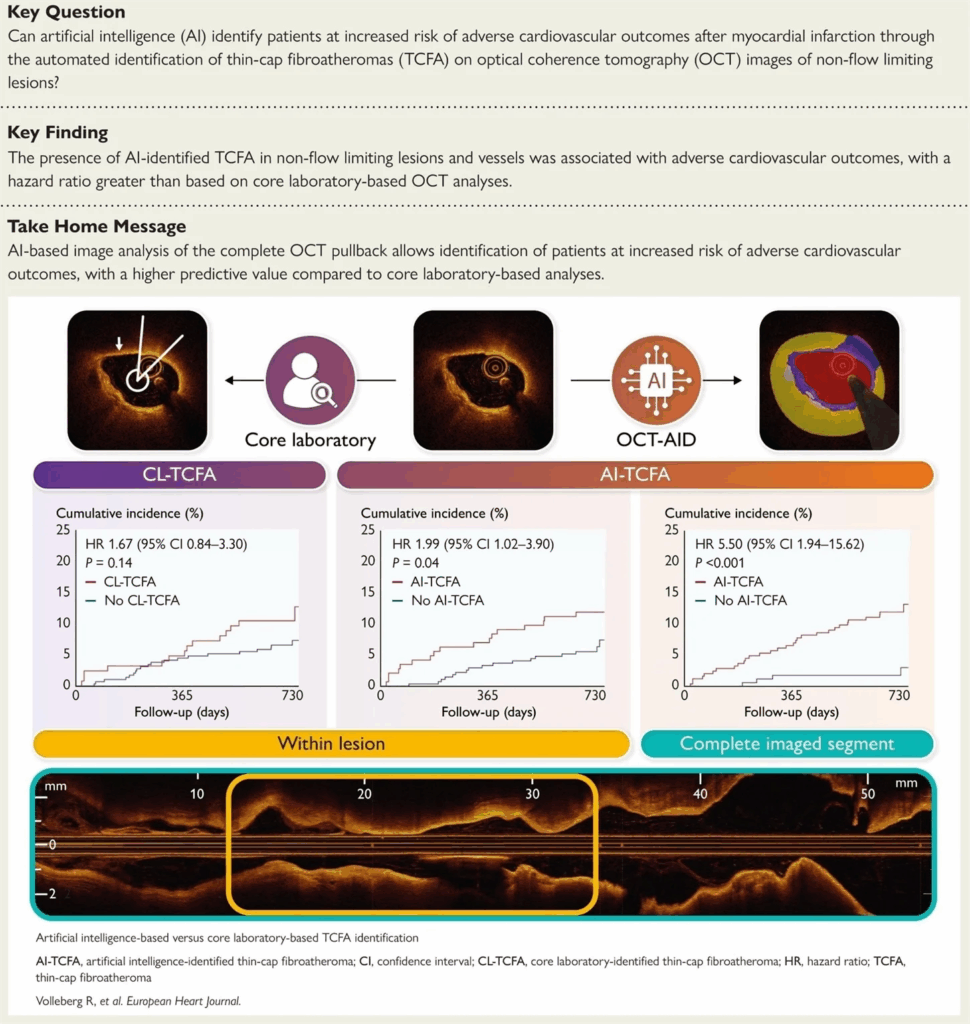
AI Scans Arteries and Predicts Risk After Heart Attack Better Than Traditional Review with AI-QCT Insights
The CONFIRM2 global study used AI-enabled quantitative coronary CT angiography (AI‑QCT) across 3,551 symptomatic patients from 18 centers. AI identified that percent diameter stenosis and non-calcified plaque volume were the strongest predictors of major adverse cardiac events (MACE), outperforming traditional calcified volume metrics.
AI Scans Arteries and Predicts Risk After Heart Attack Better Than Traditional Review with Combined Model Accuracy
Combining the PREVENT risk score with coronary calcium imaging improved predictive accuracy over either method alone. In a cohort of nearly 7,000 patients, this blended model better stratified those who went on to experience heart attacks.
This integration shows how AI enhances traditional scoring by incorporating imaging directly into risk algorithms.
AI Scans Arteries and Predicts Risk After Heart Attack Better Than Traditional Review with Mammogram-Based Detection
Stamford Health leveraged AI to detect breast artery calcification (BAC) during routine mammograms—a non-CT imaging context. Results revealed that women with BAC had a 17% higher risk of major cardiac events, adding diagnostic value while avoiding additional scans.
AI Scans Arteries and Predicts Risk After Heart Attack Better Than Traditional Review thanks to Improved CT Angio Reliability
AI-augmented coronary CT angiography—termed “bionic radiologist”—enables age‑ and gender-adjusted plaque volume percentiles, adding context-driven risk precision. This brings more reliable, cost-effective imaging and supports tailored treatment thresholds.
Why This Matters: AI vs Traditional Review in a Glance
| Approach | Traditional Review | AI-Enhanced Review |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Capabilities | Plaque size, calcification, visual analysis | Visual + hidden biomarkers (inflammation, microcalcification, plaque composition) |
| Accuracy in predicting outcomes | Moderate, often misses cases | High, catches subtle risks |
| Time to result | Delayed reporting | Near real-time analytics |
| Personalization | Generic risk scores only | Tailored patient profiles |
| Clinical impact | Often static management | Enables early, proactive treatment decisions |
Real-World Impact
In Oxford real-world tests, AI-driven CT scan analysis changed 45% of treatment decisions, leading to earlier statin use or preventive therapies—moves likely to prevent future heart attacks.
This demonstrates how AI scans arteries and predicts risk after heart attack better than traditional review isn’t just academic—it’s actively saving lives by enabling timely intervention.
Final Thoughts
AI scans arteries and predicts risk after heart attack better than traditional review because it merges precision, personalization, speed, and scalability in cardiovascular diagnostics. It’s not replacing clinicians but amplifying their insights—turning standard CTs into powerful predictive tools. As AI systems gain regulatory approval and the capability to process everyday imaging workflows, the future of heart care becomes proactive, tailored, and undeniably smarter.
External Resource (DoFollow):
For further reading on AI-enabled calcium scoring systems, see this comprehensive study on AI-CAC and cardiovascular risk: https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/advance-article/doi/10.1093/eurheartj/ehaf595/8244402?login=false
Also Read: https://aiindexes.com/apple-anthropic-ai-reasoning-showdown/